Whether you prefer beer, wine, or liquor, what you don’t know about alcohol can hurt you. Before your next drink, take a look at some facts regarding alcohol and alcohol abuse.
If you or a loved one need help, call our admissions team today at 561-841-1033.Facts about Alcohol & Alcoholism
How Common is Alcohol Use?
Alcohol is the most commonly used addictive substance in the United States: 17.6 million people, or one in every 12 adults, suffer from alcohol abuse or dependence. Every year, several million more drink heavily. Not all binge drinkers become alcoholics, but it is a risk factor.
In the past year:
- 68.6% of men over age 12 drank alcohol
- 62.9% of women over age 12 drank alcohol
- 24.9% reported binge drinking
- 6.5% reported heavy drinking
- 5.9% met the criteria for a substance use disorder (a.k.a. “alcohol abuse” or alcoholism)

Ethyl alcohol, also known as ethanol, is the intoxicating agent in alcoholic beverages. This chemical is produced from fermented yeast, sugars, and starches derived from a variety of grains, fruits, vegetables, and plants. Drinking in moderation means your liver is able to properly metabolize alcohol from your drink. Heavy drinking, however, overwhelms your liver, allowing excess amounts of alcohol to run through your body, even your brain, making you “drunk.”
Alcoholism and Healthcare
- Alcoholism is the 3rd leading lifestyle-related cause of death in the nation
- Binge drinking is responsible for 2.5 million years of potential life lost annually, or an average of about 30 years of potential life lost for each death
- Up to 40% of all hospital beds in the United States are being used to treat health conditions that are related to alcohol
- Older adults are hospitalized as often for alcohol-related problems as for heart attacks
Alcohol and Public Safety
- Nearly one-third of all traffic-related fatalities in the United States are a result of driving under the influence of alcohol
- DUIs continue to be one of the most frequent causes of arrests every year
- DUIs cost the United States more than $44 billion each year in prosecution, higher insurance rates, higher taxes, medical claims and property damage
- There are more than 2,200 alcohol overdose deaths in the United States each year—an average of six deaths every day
Signs of alcohol overdose include:
- Confusion
- Difficulty staying awake
- Vomiting
- Seizures
- Trouble breathing
- Slow heart rate
- Clammy skin
- No gag reflex (which prevents choking)
- Low body temperature
Cold showers, hot coffee, or walking will not reverse an alcohol overdose. They can actually make things worse. Don’t act alone – call 911 immediately.

The “standard” amount of alcohol in your beverage is roughly 14 grams or 0.6 ounces of pure alcohol.
By type of drink, this breaks down to:
- 5 ounces of wine (12% alcohol content)
- 12 ounces of the typical beer (5%)
- 1.5 ounces of distilled spirits (40%)
- 8 to 9 ounces of malt liquor (7%)
Unfortunately, the typical size of a beverage in a restaurant or bar doesn’t conform to standard drink sizes, meaning a single mixed cocktail could potentially contain the alcohol of 3 standard drinks.
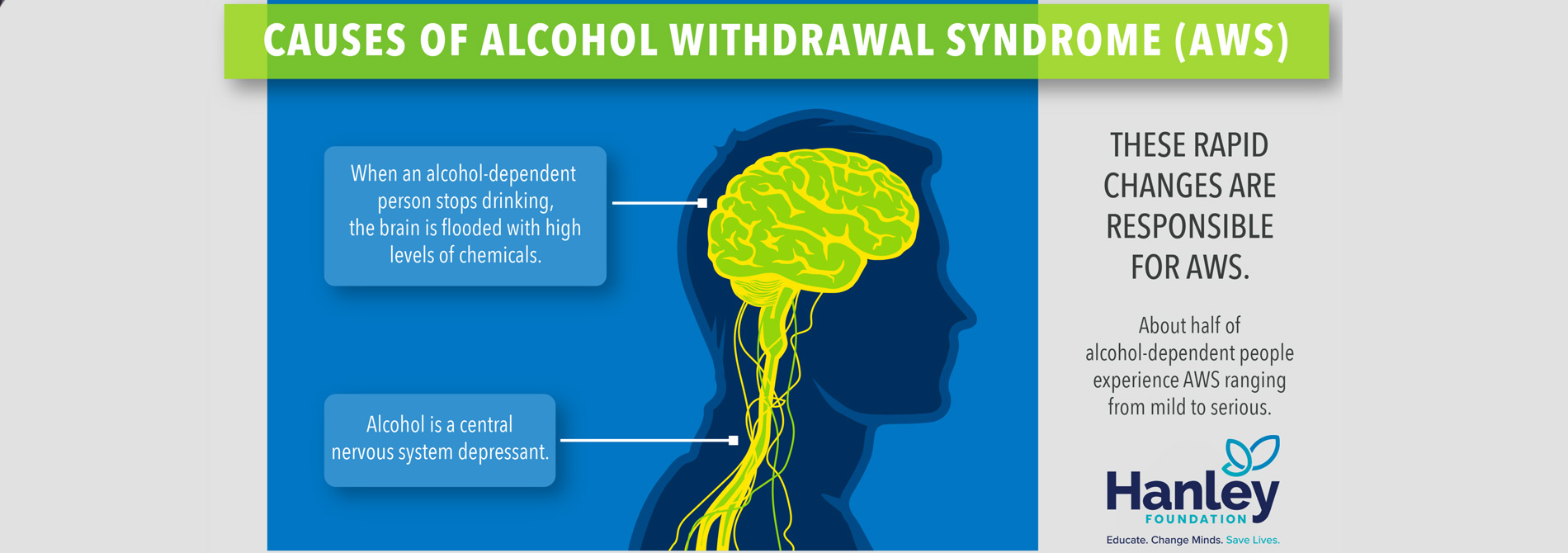
Alcohol and the Brain
Another fact about alcohol is that it causes your brain to physically adapt to your environment, allowing you to perform better at whatever you might be doing. However, when you consume alcohol on a consistent basis, your brain can interpret this as a new environment and alter nerve cells and brain connections to help you function better with alcohol in your system. IN short, once your brain adapts to alcohol, there is no going back, meaning once you stop drinking, some of these changes remain a problem for the rest of your life.
Alcohol and Gender
Due to the difference between men and women in terms of stomach enzymes, hormones, the ratio of muscle to fat, and water concentration in the body, men and women will metabolize alcohol differently.
Warning Signs of Alcoholism
Sometimes the warning signs of alcohol abuse are very noticeable. Other times, they can take longer to surface. It is important to act quickly when the warning signs appear. Catching alcoholism early can improve the chances for a healthy recovery.
Common signs of alcoholism include:
- Being unable to control your drinking
- Drinking after you’ve promised to quit
- Unsuccessfully limiting the amount you drink
- Spending less time on activities that used to be important, such as hanging out with family and friends, exercising, or pursuing hobbies or other interests
- Drinking despite consequences
- Putting alcohol above personal responsibilities and relationships
- Going out of your way to hide the amount you drink
- Drop in attendance and performance at work or school
- Needing to drink more and more in order to produce the same effect
- Withdrawal symptoms such as shakiness, trembling, sweating, nausea or fatigue
Hanley Center is a well-known care provider offering a range of treatment programs targeting the recovery from substance use, mental health issues, and beyond. Our primary mission is to provide a clear path to a life of healing and restoration. We offer renowned clinical care for mental illnesses and have the compassion and professional expertise to guide you toward lasting wellness. For information on our programs, call us today: 561-841-1033.